
Back extensions are a versatile exercise that can be used for both strength building and injury recovery. Whether you’re working on improving your lower back strength or recovering from an injury, this exercise provides a low-impact way to target key muscle groups. One of the advantages of back extensions is their equipment flexibility; they can be performed with bodyweight alone or enhanced with equipment such as resistance bands or a back extension machine for obliques. Back extension machine targets obliques and lower back, strengthening core and relieving pain with controlled movements. The back extension machine is especially useful for those who want to isolate the lower back and oblique muscles more effectively. Regardless of the method, maintaining proper form is crucial to prevent injury and maximize the benefits of the exercise, ensuring a safe and effective workout.
The back extension machine for obliques is a type of plate loaded machine that focuses on isolating and strengthening the lower back muscles, specifically the erector spinae, while also engaging the obliques for improved core stability. It provides an efficient way to perform back extensions with a focus on strengthening the spine and improving posture.
The primary focus of the back extension machine for obliques is the lower back. By isolating these muscles, the machine helps in building strength in the erector spinae, which supports the spine and aids in extension movements. In addition to the lower back, the machine activates the oblique muscles, providing a full core workout. The obliques play a key role in stabilizing the trunk and supporting rotational movements, making them crucial for both functional strength and injury prevention. When combined with exercises on the standing back row machine, which targets the upper back and posterior muscles, you can achieve a more comprehensive core and back strengthening routine.
This exercise can be performed using bodyweight, but incorporating the back extension machine for obliques allows for greater control and progression. You can add resistance through weights, resistance bands, or specialized equipment like Roman chairs or Hyperextension benches, offering multiple ways to challenge the muscles and increase difficulty. The machine ensures proper form and reduces the risk of injury compared to performing the exercise without support.
The back extension machine for obliques is highly versatile and serves dual purposes in both training and recovery programs. It is an excellent tool for those looking to enhance their back and core strength, as well as for individuals recovering from injuries. The low-impact nature of the machine allows it to be suitable for people with limited mobility or those undergoing rehabilitation, offering a safe way to rebuild strength and mobility in the lower back and obliques. For those unfamiliar with the exercise, back extension machine how to use guides can provide step-by-step instructions to ensure correct form and maximize the effectiveness of the workout.
The back extension machine for obliques is designed to target several key muscle groups that are essential for spinal support, core strength, and overall stability. This machine isolates the lower back muscles, while also engaging the obliques for improved trunk rotation and posture. By using this machine, you can effectively activate and strengthen these muscles, which play an important role in both performance and injury prevention.
The back extension machine for obliques is a powerful tool for targeting multiple muscles along the posterior chain, with a particular emphasis on strengthening the lower back and obliques. By using this machine, you can effectively work the muscles that are critical for stabilizing the spine, enhancing posture, and improving overall body strength. These muscles are involved in various movements, from lifting and bending to rotating the torso, making them essential for daily activities and athletic performance. To complement this, the thrust machine can focus on the lower body, helping to develop strength in the hips and glutes, further improving functional strength and stability.
The primary muscle group worked by the back extension machine for obliques is the low back, particularly the erector spinae. These muscles run along the spine and are responsible for spinal extension, supporting and protecting the spinal column during movement. As you extend your back in the machine, the erector spinae contract to lift your upper body, improving strength in the lower back and increasing overall spinal stability. This makes the back extension machine one of the best exercise machine for lower back, as it effectively targets and strengthens the muscles responsible for spinal support, reducing the risk of lower back pain and improving posture.
The posterior chain refers to the muscles along the back of your body, including the lower back, glutes, hamstrings, and calves. The back extension machine for obliques effectively targets these muscles as they work in coordination to extend the spine. As you perform the exercise, the glutes and hamstrings assist in extending the hips, while the calves help stabilize your position. Strengthening the posterior chain is essential for overall athletic performance, as these muscles are crucial in generating power for activities like running, jumping, and lifting.
The erector spinae is a group of three layers of muscles that run vertically along the spine. These muscles are engaged when performing back extensions and are integral for proper spine extension. The back extension machine for obliques helps target these three layers by forcing the muscles to contract in a controlled manner during each repetition. Strengthening the erector spinae improves spinal mobility, aids in posture correction, and reduces the likelihood of strain or injury during daily movements or other exercises.
The quadratus lumborum (QL) is a deep muscle located in the lower back, connecting the pelvis to the lower ribs. While it is not directly targeted by the back extension machine for obliques, the QL assists in stabilizing the spine during back extensions. It helps provide support when the torso moves and plays a role in maintaining balance. Strengthening the quadratus lumborum through this exercise helps prevent lower back discomfort and improves overall spinal stabilization. Using the lower back raise machine can further enhance QL activation by focusing on the muscles responsible for spinal support during lower back movements.
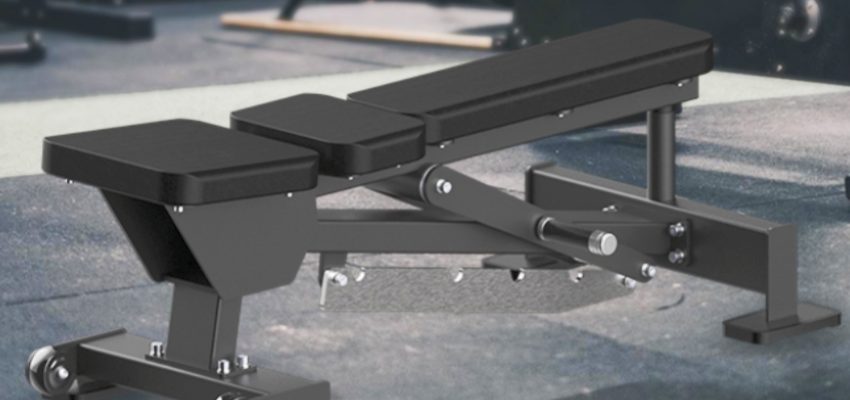
The back extension machine is typically designed to target the lower back, but with some adjustments, you can use it to engage the obliques as well. The key is incorporating a twisting or rotational movement into the exercise to specifically activate the obliques, which are responsible for the rotation and lateral flexion of the torso. Below is a step-by-step guide on how to adjust the back extension machine and modify the movement to better target the obliques:
Before beginning, ensure that the machine is adjusted correctly for your body. The back extension machine typically consists of a support pad for your hips and a footrest for your legs.
Once the machine is set up:
The primary way to activate the obliques during a back extension is by adding a rotation to the movement. The obliques are responsible for rotating the torso, so twisting at the top of the back extension movement will engage these muscles. Here’s how to perform it:
If you want to make the exercise more challenging and further target the obliques:
After completing the set of oblique-focused back extensions, it’s important to cool down and stretch your muscles to promote recovery and flexibility. Stretch your back and obliques by performing gentle side bends or other stretches that target the torso.
By adjusting the back extension machine and incorporating a twisting motion, you can effectively target your obliques while still benefiting from the lower back strengthening effects of the exercise.
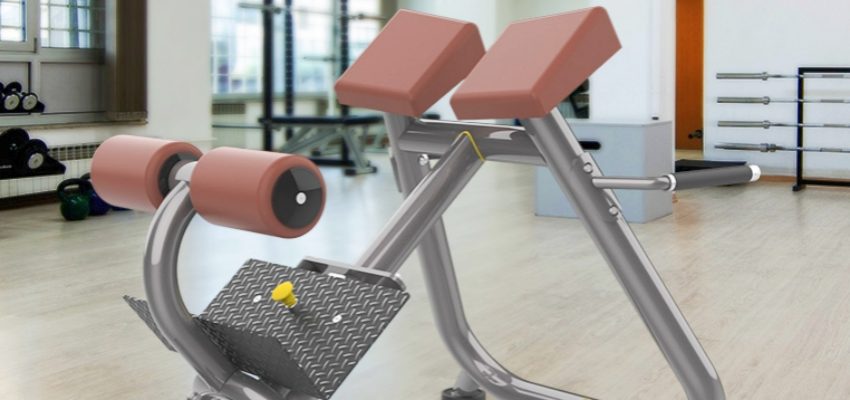

Using the back extension machine for obliques is an effective way to target the lower back and core muscles while also engaging the obliques for improved trunk stability and rotation. Here’s a detailed guide on how to perform the exercise properly, ensuring maximum benefits and safety.
Floor back extensions are a simple and effective way to begin working on your lower back and core muscles. While this variation doesn’t use the back extension machine for obliques, it lays the foundation for mastering proper form and movement mechanics. To perform floor back extensions:
This variation helps you engage the lower back, glutes, and core muscles. For advanced training, incorporating the back extension machine for obliques provides additional resistance and targeted engagement for the obliques.
Seated back extensions using the back extension machine for obliques allow you to perform a more controlled and effective movement, especially for isolating the lower back and obliques. Follow these specific form steps to maximize the benefits:
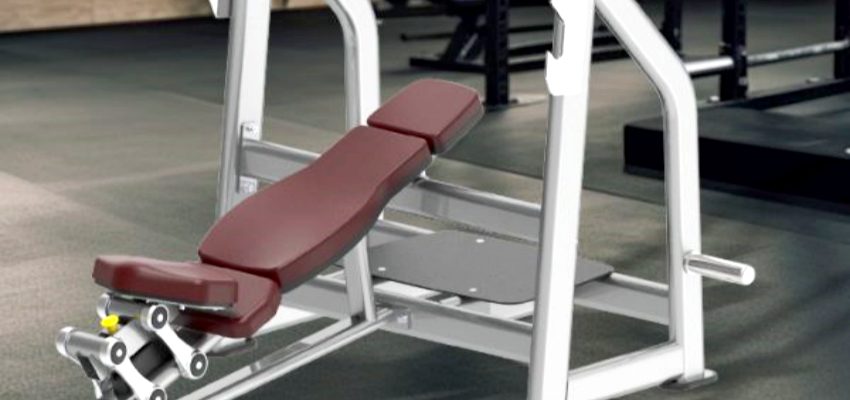

Using a 45-degree back extension machine for obliques is a great way to target your core, specifically the oblique muscles, which play a crucial role in stabilizing your torso during various movements. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to properly use this machine for oblique engagement:
By performing the exercise with controlled, deliberate movements, you can effectively engage and strengthen the obliques while also benefiting your lower back and overall core stability. Make sure to use proper form to avoid injury and ensure maximum benefits from the exercise.
The back extension machine for obliques is a versatile tool that can be adapted for different skill levels and training goals. These adaptations allow you to modify the exercise to increase intensity, target specific muscle groups more effectively, or add variety to your workout routine. Below are a few adaptations you can incorporate to enhance your back extension exercises.
Supermans are an excellent adaptation to back extensions that can be performed without equipment, focusing on the same muscle groups, but with a greater emphasis on body control. To perform Supermans:
This movement mimics the motion of a back extension but without using the back extension machine for obliques. It still activates the same muscle groups, helping build strength and stability in the lower back and core.
Incorporating weights or resistance bands into the back extension machine for obliques allows you to increase the challenge of the exercise and target your muscles more intensely. When using the machine, adding external resistance ensures continued muscle growth and strength progression.
The back extension machine for obliques offers a variety of benefits that can significantly enhance your overall fitness, posture, and injury prevention strategies. By targeting the lower back, glutes, and obliques, this exercise helps to strengthen key muscle groups that are essential for daily movement and athletic performance. Below are the key benefits of using this machine in your workout routine.
One of the primary benefits of the back extension machine for obliques is its ability to improve back stability. The exercise targets the erector spinae and oblique muscles, which are crucial for supporting the spine and maintaining proper posture. As these muscles become stronger, they provide better support to the spine, leading to improved alignment and reduced risk of slouching. Strengthening these areas also enhances your performance in other exercises, particularly those involving heavy lifting or movements requiring spinal stability, such as squats, deadlifts, and overhead presses.
By regularly using the back extension machine for obliques, you can reduce the risk of injury, particularly in the lower back. Many back injuries stem from poor posture or improper form during exercises. This machine helps you maintain correct body alignment while strengthening the muscles that protect and stabilize the spine. It also helps prevent overextension, which can strain the muscles and ligaments in the lower back. Over time, this contributes to a more resilient back and reduces the likelihood of muscle strains or sprains.
The back extension machine for obliques not only strengthens the muscles of the lower back and core, but it also improves your body awareness or proprioception. This increased awareness makes it easier to maintain a neutral spine and proper posture during other exercises. For example, when performing compound lifts or dynamic movements, a strong and well-trained core will help you keep your back straight and avoid excessive rounding or arching. This contributes to safer, more effective workouts, especially in high-intensity training.
Another significant benefit of the back extension machine for obliques is that it is a low-impact exercise, making it ideal for individuals who are recovering from back injuries or who have limited mobility. Unlike more high-impact exercises like running or jumping, the back extension machine allows you to target and strengthen key muscles without placing undue stress on the joints or spine. This makes it a safe and effective exercise for rehabilitation, as it can be performed gently and gradually as part of a recovery program. It helps improve muscle strength, mobility, and endurance while minimizing the risk of reinjury. For individuals looking to further strengthen their upper body, the plate loaded pullover machine provides a great addition to their routine, helping to enhance muscle engagement in a controlled and low-impact manner.
When using the back extension machine for obliques, it’s essential to perform the exercise with proper technique to avoid injury and maximize effectiveness. Improper form or misuse of equipment can lead to unnecessary strain, reducing the benefits of the exercise. Here are some common mistakes to avoid while performing back extensions.
One of the most common mistakes when using the back extension machine for obliques is hyperextending the back. Hyperextension occurs when you bend the spine too far beyond its neutral position, creating an excessive arch in the lower back. This puts unnecessary stress on the vertebrae, discs, and surrounding tissues, increasing the risk of injury. To avoid hyperextension:
By ensuring your back remains neutral and avoiding hyperextension, you protect your spine from undue stress and promote a safer, more effective workout.
Another mistake to avoid when using the back extension machine for obliques is careless weight usage. Adding too much weight or using resistance that is too heavy for your current strength level can strain your lower back, glutes, or obliques, leading to potential injury. To safely increase resistance:
Yes, back extensions do work the obliques, especially when performed on a back extension machine for obliques. While the primary target of back extensions is the lower back (specifically the erector spinae), the movement also engages the core, including the obliques. The obliques are responsible for stabilizing and rotating the trunk during the exercise, especially if you add a twisting or side-bending motion during the extension. This engagement helps strengthen the lateral muscles of the core, which are essential for maintaining good posture, balance, and rotation. To specifically target the obliques, you can incorporate variations like twisting back extensions, where you rotate your torso at the peak of the movement. By focusing on controlled, deliberate motions, you ensure both the lower back and the obliques get a balanced workout. However, for more targeted oblique training, adding resistance or using machines designed for oblique exercises, such as cable rotations or side crunch machines, may be more effective.
Several gym machines target the obliques, each offering different approaches to strengthening these essential core muscles. A back extension machine for obliques can be effective, especially if you incorporate a twisting motion into the back extension. The twisting motion engages the obliques while also working the lower back. Another machine that specifically targets the obliques is the torso rotation machine. This machine allows you to perform seated rotations, which isolates the obliques by having you twist your torso against resistance. Additionally, cable machines with a rope attachment can be used for cable woodchops or side rotations, which activate the obliques during a twisting motion. Ab crunch machines, when used with proper form, also help engage the obliques by allowing you to perform lateral crunches, targeting both the obliques and the rectus abdominis. Combining these machines in your routine provides variety and comprehensive engagement of the core.
Yes, you can use a back extension machine for obliques to work the abdominal muscles, although the primary focus is on strengthening the lower back. The machine targets the erector spinae (lower back muscles), but the core, including the abs, is engaged as stabilizers throughout the movement. For abs specifically, it’s important to maintain good form by keeping your core tight during the exercise. To target the abs more effectively on the back extension machine for obliques, you can try incorporating slight forward flexion as you reach the top of the movement. This will engage the rectus abdominis (the “six-pack” muscles) more intensely. While the back extension machine for obliques isn’t typically used as a primary tool for abs, it does contribute to strengthening the entire core, including the lower abs. For more focused ab work, you may want to complement back extensions with exercises like crunches, leg raises, or other ab-specific machines.
The back extension machine for obliques primarily works the muscles along the posterior chain, with a focus on the lower back, glutes, and core. The main muscles targeted are the erector spinae, which are the muscles that run along the spine and are responsible for spinal extension. These muscles help in straightening and stabilizing the back. As you perform back extensions on the machine, the erector spinae engage to lift your torso, strengthening the lower back. Additionally, the glutes and hamstrings are activated as they help extend the hips, providing support and stability during the movement. The obliques, while not the primary focus, are engaged as stabilizers of the trunk, especially if you incorporate twisting motions or side bends into your back extension. Other secondary muscles that benefit from the exercise include the quadratus lumborum (a deep stabilizing muscle in the lower back), and the calves that assist in maintaining posture. Overall, the back extension machine for obliques provides a comprehensive workout for the lower back, core, and posterior chain.D
Back extensions primarily target the lower back muscles, such as the erector spinae, and also engage the glutes and hamstrings. However, they can also indirectly activate the obliques, especially if performed with added rotation. The obliques are responsible for the rotation and lateral flexion of the torso, so if you add a twisting motion during the back extension, you can engage these muscles. To activate the obliques during back extensions, rotate your upper body to one side while extending your back, and alternate sides with each repetition. By incorporating this twist into your movement, you create a more dynamic motion that engages not just the lower back, but also the obliques and side muscles. However, the back extension machine is not primarily designed to isolate the obliques, and you may not achieve as much engagement as with exercises specifically targeting the side muscles, such as side crunches or cable woodchoppers. Nevertheless, incorporating a slight rotation during back extensions can be a useful addition to your routine, providing a supplementary workout for your obliques while also strengthening the lower back.
The obliques play a key role in lateral flexion, rotation, and trunk stabilization, rather than extending the spine. The oblique muscles consist of two groups: the external obliques and internal obliques, which are located on either side of the torso. Their primary function is to assist in bending the torso sideways (lateral flexion) and rotating it. For example, when you perform exercises like side bends or rotational movements such as Russian twists, the obliques contract to help perform these motions. In addition, the obliques play an important role in stabilizing the spine, especially during activities that require torsional movements, like lifting or twisting. The internal obliques, which are located beneath the external obliques, work together with the external obliques to facilitate rotational movements of the torso. They do not play a significant role in the extension of the spine. In summary, while the obliques do not extend the back, they are heavily involved in flexing the torso laterally and rotating it, as well as maintaining core stability.
Yes, the obliques are connected to muscles in the lower back. The external obliques, located on the sides of the torso, have muscle fibers that run diagonally across the abdomen and the back. These fibers are designed to help rotate the trunk and assist in lateral flexion. While the obliques themselves do not directly “go into” the back, their anatomical structure means that they are closely intertwined with muscles that surround the back. The internal obliques, which lie beneath the external obliques, contribute even more to the rotational and lateral bending actions of the torso. They also play a role in maintaining spinal stability and support. These muscles are intimately connected to the erector spinae, the primary muscle group responsible for lower back extension. The function of the obliques, therefore, has a direct influence on the back, especially when engaging in movements like twisting, rotating, or bending sideways. Though the obliques themselves do not extend into the back muscles, their actions and connections help to stabilize and facilitate movement across the entire torso, including the spine and lower back.
To use the back extension machine for targeting the obliques, it’s important to introduce a rotational element to the movement. While the back extension primarily targets the lower back muscles (erector spinae), you can modify the exercise to engage the obliques. Here’s how to do it:
Position yourself correctly: Start by adjusting the back extension machine so that the pads support your hips, ensuring you have a full range of motion for your torso.
Perform the basic back extension: Begin with a standard back extension by hinging at the hips and extending your torso upward.
Incorporate a twist: At the top of the back extension, rotate your torso to one side while keeping your arms extended in front of you or holding a weight plate for added resistance. This twisting motion activates the obliques, as they are responsible for trunk rotation.
Alternate sides: After completing one side, return to the starting position and repeat the twist on the other side.
Focus on control: Perform the movement slowly and with control to fully engage the obliques. Avoid jerking your body during the twist, as this could reduce the effectiveness and strain the lower back. Adding this rotational element to the back extension machine provides a way to target your obliques while also strengthening your lower back. However, for more focused oblique work, you should include other exercises like side crunches, cable woodchoppers, or Russian twists.
While the back extension machine is not designed to target the abs directly, you can modify the exercise to engage the abdominal muscles more effectively. The key is to focus on core activation during the movement. Here’s how you can use the back extension machine for working your abs:
Set up the machine: Position yourself on the back extension machine with your hips against the pad and your feet secured. Adjust the height of the machine so your hips are fully supported, and you have a full range of motion for your torso.
Engage your core: As you begin the extension, tighten your core (abs and lower back muscles). Focus on engaging the abdominal muscles as you extend your torso upward. The key to engaging your abs is to maintain a braced core, avoiding excessive arching of the back.
Add a crunch at the top: Once you reach the top of the back extension, perform a small crunch by slightly bending your upper body forward and contracting your abs. This mimics the action of a crunch and helps engage your abdominal muscles more directly.
Slowly lower your torso: Return to the starting position, maintaining tension in your core throughout the movement. While back extensions do work the core muscles to some degree, they are not as effective at isolating the abs compared to other abdominal exercises. For better abs activation, it’s recommended to combine back extensions with traditional core exercises like crunches, leg raises, or planks.
A cable machine is an excellent tool for targeting the obliques because it allows you to perform rotational movements that directly engage these muscles. Here’s how to target your obliques using a cable machine:
Set up the cable machine: Attach a rope or single handle to a high pulley on the cable machine.
Adjust your stance: Stand perpendicular to the machine with your feet shoulder-width apart. Hold the handle with both hands and pull it across your body, keeping your arms straight and your torso engaged.
Rotate your torso: Keeping your arms extended in front of you, rotate your torso to pull the handle across your body and to the opposite side. This rotation activates your obliques, which are responsible for torso twisting movements.
Return slowly: After reaching the maximum point of rotation, return the handle to the starting position slowly, resisting the pull of the cable to maintain tension in the obliques.
Repeat: Perform 10–15 reps on one side before switching to the other side to target both obliques. You can adjust the height of the cable to target different parts of the obliques, such as high cable rotations for upper obliques or low cable rotations for lower obliques. Additionally, adding more weight can increase the challenge and provide a more intense workout for your obliques.
Although the back extension machine is primarily designed to strengthen the lower back, it can indirectly work the abs. While performing the exercise, your core must engage to stabilize your torso and prevent any excessive arching of the back. However, for direct ab work, the back extension machine is not as effective as exercises that specifically target the abdominal muscles. To enhance the ab engagement during back extensions, you can focus on tightening your core throughout the movement. Additionally, incorporating a small crunch at the top of the extension can further activate the abdominal muscles. While back extensions provide a good overall core workout, for better isolation of the abs, it’s best to include traditional ab exercises such as planks, crunches, or leg raises in your routine. These exercises are more effective at directly targeting and strengthening the abdominal muscles.
While the back extension machine can be a valuable tool for strengthening the lower back, there are some potential drawbacks that should be considered:
Risk of improper form: If not used properly, the back extension machine can put unnecessary strain on the spine. Overextending or jerking the back during the movement can lead to injuries such as strains or sprains, particularly in the lower back. It’s important to use proper form and avoid hyperextending the back.
Limited muscle focus: The back extension machine primarily targets the lower back (erector spinae), glutes, and hamstrings. However, it does not engage the upper back, shoulders, or abdominal muscles as effectively as other exercises. For a more balanced workout, it’s important to incorporate exercises that target other muscle groups as well.
Overuse leading to muscle imbalances: Focusing too much on back extensions without balancing your workout with exercises for the upper body and core can lead to muscle imbalances. Strengthening the lower back is important, but it’s also essential to work on your abs, upper back, and other muscle groups to avoid creating imbalances that could result in poor posture or injury.
Not ideal for beginners: For those who are new to strength training or have lower back issues, the back extension machine might not be the best choice. It’s important to build up core strength with more basic exercises before attempting more advanced movements like back extensions. Starting with bodyweight exercises such as planks or bird dogs may be a safer option for beginners.
Side crunches on the back extension machine are a great way to target your obliques while also working the lower back muscles. To perform side crunches on the back extension machine, follow these steps:
Position yourself: Adjust the machine so that the pads are securely positioned just below your hips. Stand sideways to the machine, with one side of your body facing the pads.
Engage your core: Hold onto the handles for stability, and keep your torso straight. Ensure that your core is engaged as you begin the movement.
Perform the side crunch: As you extend your body upward, twist your torso to one side, crunching your oblique toward the machine. Keep your movements slow and controlled to maximize the engagement of the obliques.
Return to starting position: Slowly return to the starting position, keeping your torso engaged throughout the movement. Repeat the side crunch for the desired number of repetitions.
Switch sides: After completing one side, turn around and perform the same movement on the opposite side to target the other oblique.
By adding a twisting motion while performing back extensions, you can effectively work the obliques and add variety to your routine.
Yes, back extensions work the core to some extent, although they primarily target the lower back muscles (erector spinae), glutes, and hamstrings. The core plays a stabilizing role during the exercise to protect the spine and maintain proper posture throughout the movement. When performing a back extension, the abdominal muscles, including the transverse abdominis and rectus abdominis, contract to support the spine and help prevent overextension. While the back extension machine does not specifically isolate the abs, it indirectly activates the core as you engage it to keep the body in a neutral position. To maximize core activation, it’s important to focus on maintaining a braced core during the entire movement. To enhance core work, you can add variations, such as including a small crunch at the top of the extension or performing the exercise with added resistance. However, for more targeted abdominal training, exercises like crunches, planks, or leg raises are more effective for isolating and strengthening the abs.
Yes, a torso rotation machine can be a good tool for targeting the obliques and working the muscles of the core, especially the muscles responsible for rotation. The machine allows for controlled, repetitive twisting movements, which are ideal for activating the obliques. The obliques are key muscles in the torso that assist in rotational movements and lateral flexion of the spine. By using a torso rotation machine, you can focus on these twisting motions to build strength and definition in the obliques. Additionally, since the machine offers resistance during the rotation, it can help enhance the muscle-building process. However, it’s important to use proper form to avoid over-rotating and placing undue stress on the spine. The torso rotation machine works primarily on the obliques, but it does not fully target all parts of the abdominal muscles. For complete core development, it’s best to incorporate additional exercises, such as planks, crunches, or leg raises, into your routine for balanced abdominal strength.
Back extensions are not directly effective for targeting fat in the lower back. The concept of spot reduction, which suggests that you can lose fat from specific areas of the body by performing exercises targeting that region, is a common misconception. Fat loss occurs as a result of a caloric deficit, and it is not possible to selectively burn fat from particular areas of the body. While back extensions strengthen the lower back muscles, including the erector spinae, glutes, and hamstrings, they do not directly target fat loss in the lower back. However, strengthening the muscles of the lower back through back extensions can improve posture and overall body composition, making it easier to achieve a leaner appearance when combined with a balanced exercise routine and a healthy diet. To reduce fat in the lower back area, you should focus on overall fat loss strategies, including cardiovascular exercise, full-body strength training, and maintaining a caloric deficit.
To work on your abs without bending your back, it’s important to focus on exercises that engage the core without requiring spinal flexion or extension. Here are some exercises that can help you achieve this:
Planks: The plank is a great exercise that works the entire core, including the abs, obliques, and lower back, without requiring any bending of the spine. To perform a plank, hold a straight line from head to heels, keeping your core engaged to maintain stability.
Dead bugs: This exercise involves lying on your back and extending one arm and the opposite leg at the same time, while keeping your spine neutral and stable. The movement targets the core without putting strain on the back.
Bird dogs: In this exercise, you extend one arm and the opposite leg while keeping your back straight and your core engaged. This is a great way to work the abs and stabilize the spine without flexion or extension.
Leg raises: Lying flat on your back, lift your legs while keeping your core tight and your back pressed to the floor. This isolates the lower abdominal muscles without involving any bending of the back. These exercises allow you to engage your abdominal muscles and strengthen your core without stressing or bending the spine. They are effective for building a strong, stable core while avoiding unnecessary back movements.
The back extension machine is primarily designed to work the muscles of the lower back, particularly the erector spinae, which runs along the spine and helps with spinal extension. However, the machine also engages several other muscle groups during the movement:
Erector Spinae: These muscles, located along the spine, are responsible for extending and stabilizing the lower back. They are the primary muscles targeted during the back extension.
Glutes: The gluteal muscles are engaged as you extend your hips, providing power and stability during the movement.
Hamstrings: The hamstrings assist in hip extension, working alongside the glutes to perform the movement.
Core muscles: The abdominal muscles, including the rectus abdominis and transverse abdominis, play a stabilizing role to protect the spine and maintain proper posture during the exercise. While the back extension machine is mainly used to strengthen the lower back, it also provides some engagement of the glutes, hamstrings, and core muscles, making it a beneficial exercise for improving overall lower body and core strength.
Hip extension and back extension are two distinct movements that target different muscle groups and involve different motion patterns:
Hip Extension: Hip extension refers to the movement of the leg backward, away from the body, involving the hip joint. This movement primarily targets the glutes, hamstrings, and hip flexors. Exercises such as glute bridges, deadlifts, and hip thrusts emphasize hip extension by focusing on the movement at the hip joint while keeping the back neutral.
Back Extension: Back extension, on the other hand, refers to the movement of the torso (upper body) backward, away from the thighs. It primarily targets the erector spinae muscles along the spine, which are responsible for spinal extension, as well as engaging the glutes and hamstrings to assist in the movement. The key difference lies in the joint action: hip extension involves moving the leg, while back extension involves the upper body. Both exercises are beneficial for improving strength in the posterior chain, but they focus on different areas of the body.
The back extension machine is primarily designed to strengthen the lower back muscles, including the erector spinae. While it does work the core muscles to a certain extent by requiring stabilization during the movement, it is not the best exercise for isolating the abdominal muscles. The core plays a crucial role in stabilizing the body during the back extension, and the abdominals work to maintain a neutral spine and prevent excessive arching. However, the back extension machine does not directly target the abs in the way exercises like crunches, planks, or leg raises do. To use the back extension machine for core work, focus on engaging your abs throughout the movement by bracing your core and avoiding overextension. Additionally, you can add a small crunch at the top of the extension to increase abdominal activation. While the back extension machine can provide some core engagement, it is best complemented with other ab exercises for a well-rounded core workout.
The back press machine primarily targets the shoulders and arms, particularly the deltoids, trapezius, and triceps. Depending on the variation of the back press (overhead press or behind-the-neck press), it can work different parts of the shoulder and upper back. Here’s a breakdown of the primary muscles involved:
Deltoids: The deltoid muscles, which consist of the anterior, lateral, and posterior parts, are the primary muscles worked during the back press machine exercise. The anterior deltoid is especially activated during overhead presses, while the lateral and posterior deltoids contribute to the movement as well.
Trapezius: The upper trapezius muscles in the upper back assist in stabilizing the shoulder blades during the pressing motion.
Triceps: The triceps muscles of the upper arms are responsible for extending the elbows during the pressing motion, providing support to the shoulder muscles.
Rotator cuff: The rotator cuff muscles help stabilize the shoulder joint and allow for smooth, controlled movement during the press. The back press machine is an effective tool for building strength and muscle mass in the shoulders, upper chest, and arms, but it does not target the lower body or core as directly as other exercises.
I’m Jessica Camp, a passionate fitness enthusiast and the creative force behind Inpek Fitness’s content. With over a decade in the fitness industry, I combine my expertise in exercise science with a deep knowledge of commercial gym equipment. I’m dedicated to promoting health and wellness by sharing valuable tips, training techniques, and the latest trends in Pin Loaded Machines, Plate Loaded Machines, Multi Function Gym Machines, Gym Multi, and Free Weights. Whether you’re a gym owner or a fitness enthusiast, my articles are crafted to inspire and empower you to reach your fitness goals. When I’m not writing, I love working out and exploring innovative fitness solutions.
Looking to enhance your gym with premium equipment? Have inquiries or ideas? Complete the form below to engage with our expert team. We’ll work with you to realize your fitness facility goals efficiently and effectively.