Wholesale Back Extension Machines & Ab Crunch Machines
- Home
- /
- Back extension machines & Ab crunch machines
High-quality back extension machines and abdominal curl machines work your core and lower back for a stronger, more defined look. Designed for optimal performance, these machines help you build strength, improve posture, and enhance stability while ensuring comfort and safety. Whether you’re working your lower back, glutes, and hamstrings with the back extension machine or your abdominals and obliques with the abdominal curl machine, our equipment offers the perfect combination of support and results.
Our back extension machines feature adjustable settings, allowing users of all sizes to customize their workouts. These machines provide a comprehensive core workout while stimulating the glutes, hamstrings, and even abdominal muscles for a well-rounded strength training experience. Designed for comfort and versatility, they ensure proper posture and fluid movement, making them an essential tool for core training and injury prevention.
Our abdominal curl machines take core training to the next level with ergonomic padding, adjustable resistance, and a stable design that isolates the abdominal muscles. By minimizing the involvement of stabilizing muscles, these machines allow for better muscle activation and control of movement, making them ideal for both beginners and advanced athletes. With preset weights and guided movements, you can train effectively and safely, bridging the gap between bodyweight exercises and progressive overload.
At Inpek Fitness, we are committed to providing commercial-grade equipment that meets the highest standards of durability, safety, and innovation. With decades of expertise since 1996, we offer comprehensive fitness solutions, personalized customization, and fast global shipping. Our dedication to value, independent innovation, and green solutions ensures that every piece of equipment enhances your fitness journey.
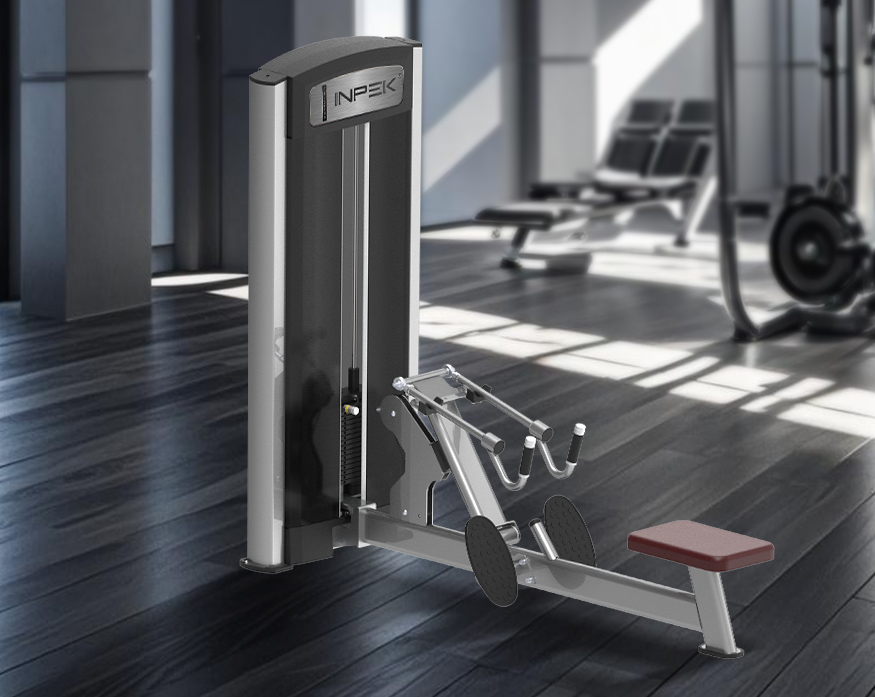


What to Consider When Wholesaling Back Extension Machines & Ab Crunch Machines
Consider When Wholesaling Back Extension Machines
Wholesaling gym back machines for your gym is a significant investment, and it’s essential to consider several factors to ensure you’re making the right choice. Here’s what you should pay attention to:
Weight Capacity and Durability
Ensure the back extension machine can handle the maximum weight your users will lift. Our machines are built with heavy-duty materials to support high weight limits, providing a safe and stable workout experience.
Space Requirements
Measure your available space to ensure the machine fits comfortably. Our back extension machines are designed to be compact and space-saving, making them ideal for gyms of all sizes.
Customization Options
At Inpek Fitness, we offer customizable solutions to help you find the perfect back extension machine that aligns with your gym’s aesthetic and functional needs.
Budget and Pricing
Our range of back fitness machine is suitable for every budget, from affordable to premium models. Compare prices and features to find the best machine for your money.
User Feedback and Reviews
Consider the feedback and reviews from other gym owners who have purchased back extension machines. Our machines are highly rated for their durability, performance, and user-friendly design.
By following these guidelines, you can confidently wholesale back extension machines for your gym and provide your clients with an exceptional workout experience.
Consider When Wholesaling Ab Crunch Machines
Wholesaling ab crunch equipments for your gym is a significant investment, and it’s essential to consider several factors to ensure you’re making the right choice. Here’s what you should pay attention to:
Weight Capacity and Durability
Ensure the ab crunch machine can handle the maximum weight your users will lift. Our machines are built with heavy-duty materials to support high weight limits, providing a safe and stable workout experience.
Space Requirements
Measure your available space to ensure the machine fits comfortably. Our ab crunch machines are designed to be compact and space-saving, making them ideal for gyms of all sizes.
Customization Options
At Inpek Fitness, we offer customizable solutions to help you find the perfect ab crunch machine that aligns with your gym’s aesthetic and functional needs.
User Feedback and Reviews
Consider the feedback and reviews from other gym owners who have purchased abdominal crunch exercise machines. Our machines are highly rated for their durability, performance, and user-friendly design.
By following these guidelines, you can confidently wholesale ab crunch machines for your gym and provide your clients with an exceptional workout experience.
Benefits of Using Back Extension Machines for Back Stretching
The back extension machine is a valuable tool for strengthening and stretching the lower back. It not only helps develop core stability but also improves flexibility, reduces the risk of injuries, and enhances overall athletic performance. Whether you are looking to strengthen your lower back muscles, improve posture, or prevent back pain, incorporating this machine into your workout routine can provide significant benefits. Below, we explore these advantages in greater detail.
Strengthens the Lower Back
How It Helps:
- By regularly performing back extension exercises, you can increase muscular endurance and strength, making everyday movements like bending, lifting, and twisting easier.
- Strengthening the lower back also helps prevent common issues such as lower back pain and muscle imbalances, which can occur due to prolonged sitting or poor posture.
- For those involved in sports or weightlifting, a strong lower back is crucial for movements such as deadlifts, squats, and other compound exercises.
Improves Posture
Poor posture is a common issue caused by prolonged sitting, weak back muscles, and incorrect spinal alignment. The back extension machine helps correct and maintain proper posture by strengthening the muscles responsible for spinal stability.
How It Helps:
- When used correctly, the machine encourages users to engage their core and maintain a neutral spine, reinforcing good posture habits.
- It strengthens the lumbar and thoracic spine muscles, which support an upright and balanced posture.
- Over time, regular back extension exercises help reduce slouching and discomfort caused by poor posture, especially for individuals who sit for long hours.
Reduces Risk of Injury
Weak back muscles are a leading cause of injuries, especially during strenuous physical activities or heavy lifting. The back extension machine helps mitigate these risks by strengthening the lower back and core muscles, which are essential for injury prevention.
How It Helps:
- Strengthening the lower back with controlled movements improves muscle resilience, reducing the likelihood of strains, sprains, and other back-related injuries.
- The machine promotes safe and controlled spinal movement, helping users develop proper mechanics for daily activities and sports.
- By incorporating this machine into a workout routine, individuals can build a more stable core and lower back, decreasing the risk of unexpected injuries.
Enhances Athletic Performance
A strong and stable lower back is crucial for athletic movements that require power, agility, and endurance. The back extension machine provides a targeted way to build back strength, which translates to improved performance in various sports and physical activities.
How It Helps:
- Many sports, such as weightlifting, running, and cycling, rely on a strong lower back to maintain proper form and prevent fatigue.
- Athletes who use the back extension machine can develop better posture and endurance, allowing them to perform at higher levels with reduced injury risk.
- The machine also helps in developing coordination between the lower back, core, and glutes, which is essential for explosive movements such as sprinting and jumping.
Low-Impact Exercise
One of the key benefits of the back extension machine is that it provides an effective workout without putting excessive stress on the joints. This makes it suitable for individuals of all fitness levels, including those recovering from injuries.
How It Helps:
- Unlike high-impact exercises that can strain the spine, the back extension machine allows for controlled, low-impact movement, reducing stress on the lower back.
- It is an excellent option for rehabilitation programs, helping individuals recover from back injuries or surgeries while still strengthening their muscles.
- Because of its low-impact nature, the machine is ideal for older adults or individuals with joint issues who need a safe and effective way to strengthen their lower back.
The back extension machine is a versatile and effective tool for strengthening the lower back, improving posture, reducing injury risk, enhancing athletic performance, and providing a low-impact workout option. Whether you’re a fitness enthusiast, an athlete, or someone looking to improve back health, incorporating this machine into your routine can yield long-term benefits. For gym owners, investing in a back extension machine can attract more clients and provide them with an essential tool for their fitness journey.

Muscles Targeted by Back Extension Machines
The back extension machine is a powerful tool for strengthening the lower back, glutes, hamstrings, and core muscles, making it an essential part of any fitness routine. By isolating and activating key muscle groups, this machine helps improve spinal stability, posture, and overall lower-body strength. Whether you’re recovering from an injury, aiming to prevent back pain, or looking to enhance athletic performance, understanding the specific muscles targeted by the back extension machine is crucial for maximizing its benefits. Below, we break down each muscle group in detail.
Erector Spinae – Strengthening the Lower Back
The erector spinae are the primary muscles activated during back extension exercises. These muscles run along both sides of the spine and play a vital role in spinal extension, stability, and posture maintenance.
- Spinal Extension: The erector spinae muscles work to extend the spine, allowing the torso to return to an upright position from a forward-bent posture.
- Postural Support: Strengthening these muscles improves postural alignment, reducing the risk of slouching and back pain.
- Injury Prevention: A strong erector spinae can protect the lower back from injuries caused by poor posture or improper lifting techniques.
By consistently training with a back extension machine, individuals can reduce lower back strain, improve spinal mobility, and enhance overall back strength.
Gluteus Maximus – Powering Hip Extension
The gluteus maximus, the largest muscle in the buttocks, plays a crucial role in hip extension and lower body strength. While primarily known for its function in leg movement, it also contributes significantly to back extension exercises.
- Hip Drive and Power: As the torso extends upward during the exercise, the glutes engage to drive the hips forward, completing the movement.
- Lower Back Support: Strong glutes reduce stress on the lower back by sharing the load during movement, preventing overuse of the erector spinae.
- Improved Athletic Performance: Strengthened glutes enhance explosive movements such as sprinting, jumping, and weightlifting.
Engaging the gluteus maximus in back extensions ensures balanced muscle development and reduces the risk of lower back pain due to weak hip muscles.
Hamstrings – Stabilizing the Lower Body
The hamstrings, located at the back of the thighs, assist in hip extension and knee stabilization during back extension movements. These muscles work in coordination with the glutes and lower back to control movement and maintain balance.
- Assisting Hip Extension: The hamstrings work alongside the gluteus maximus to extend the hips as you lift your torso.
- Providing Stability: They help maintain balance and prevent excessive lower back arching during the exercise.
- Preventing Injury: Strengthening the hamstrings reduces the risk of muscle imbalances and hamstring strains, which are common in activities that require sudden acceleration or deceleration.
Proper hamstring activation ensures smooth and controlled movements, allowing for a safer and more effective back extension workout.
Core Muscles – Supporting Stability and Balance
The core muscles, including the rectus abdominis (abs), obliques, and deep stabilizers like the transverse abdominis, play a significant role in spinal stability and movement control during back extensions.
- Spinal Stability: The core muscles prevent excessive spinal arching and help maintain proper posture throughout the exercise.
- Increased Control and Balance: Engaging the core improves body control, ensuring that movements are smooth and precise.
- Reduced Lower Back Strain: A strong core distributes pressure evenly, preventing over-reliance on the lower back muscles and reducing the risk of discomfort or injury.
By keeping the core engaged during back extensions, users can enhance overall balance, posture, and injury prevention.
The back extension machine is a valuable tool for strengthening the lower back, glutes, hamstrings, and core, making it essential for improving posture, spinal health, and athletic performance.
By incorporating back extension exercises into your routine, you can build a strong, resilient lower back, reduce pain, and improve overall functional strength for both daily activities and athletic movements.
How to Use Back Extension Machines and Adjust Them Correctly
The back extension machine is an essential piece of equipment designed to strengthen the lower back, improve posture, and enhance core stability. However, to maximize its benefits and minimize injury risks, it is crucial to use the machine with the proper form and adjustments. This guide will walk you through the correct usage, adjustments, and common mistakes to avoid for an effective and safe workout.
Correct Posture and Steps
Maintaining the correct posture while using the back extension machine ensures that you effectively target the erector spinae muscles without straining your lower back. Following the right steps will help you perform the exercise safely and get the most out of your workout.
Step-by-Step Guide:
- Positioning:
- Lie face down on the machine with your hips resting on the padded support. Your upper thighs should also be supported, but your waist should be free to move.
- Secure your feet firmly under the footpads to maintain stability throughout the movement.
- Movement Execution:
- Begin by lowering your upper body slowly toward the floor while keeping your back straight. Avoid excessive rounding of the spine.
- Engage your lower back and glutes to lift your torso back up until your body forms a straight line. Avoid hyperextending beyond a neutral spine position.
- Breathing Technique:
- Inhale as you lower your upper body down.
- Exhale as you lift your torso back up to the starting position.
- Proper breathing helps maintain core engagement and prevent strain.
Adjusting the Machine
Making proper adjustments to the back extension machine ensures that you are positioned correctly for optimal effectiveness and safety. Improper settings can lead to discomfort or potential injury.
Key Adjustments to Consider:
- Hip Pad Position:
- Adjust the hip pad so that it sits directly below your hip bones. If the pad is too high, it may restrict movement; if too low, it may reduce stability and effectiveness.
- Footpad Height:
- Ensure the footpads are positioned to secure your feet comfortably without excessive pressure. Your feet should remain in place throughout the movement.
- Angle Adjustment (if applicable):
- Some machines offer adjustable angles for different intensity levels. Beginners should start with a smaller range of motion before progressing to a deeper extension.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Even with proper machine setup, poor execution can lead to discomfort or injury. Being aware of common mistakes can help you perform the exercise safely and effectively.
Overarching the Back:
- Avoid lifting your torso too high, as this puts excessive strain on the lower back and reduces muscle activation efficiency.
- Instead, focus on stopping at a neutral spine position, where your body forms a straight line from head to toe.
Using Momentum:
- Many users make the mistake of using rapid, jerky movements, which reduces muscle engagement and increases the risk of injury.
- Always perform the exercise in a slow, controlled motion, focusing on muscle contraction rather than speed.
Incorrect Hip Alignment:
- If your hips are not properly aligned with the pad, you may feel discomfort or place unnecessary pressure on the lower spine.
- Ensure your hips are positioned just above the support pad to allow a full range of motion without restriction.
The back extension machine is a powerful tool for strengthening the lower back and improving overall spinal health. However, proper setup and execution are essential to reap its benefits safely. By maintaining the correct posture, making necessary adjustments, and avoiding common mistakes, you can ensure a safe and effective workout that supports long-term back health.

How Much Weight Should You Use on Back Extension Machines?
Selecting the right weight for a back extension machine is crucial for maximizing strength gains while minimizing the risk of injury. The appropriate weight depends on factors such as fitness level, experience, and individual goals. Whether you’re focusing on building endurance, strengthening the lower back, or increasing muscle mass, adjusting the resistance correctly will ensure safe and effective training. Below, we break down the recommended weight ranges based on different experience levels.
Beginners – Mastering Form and Building a Foundation
For beginners, the primary focus should be on proper form and muscle engagement rather than adding heavy resistance. Mastering the movement pattern first will ensure safe progression and injury prevention.
- Start with Bodyweight: Perform back extensions without any added weight to develop strength and control in the lower back, glutes, and hamstrings.
- Repetitions and Sets: Aim for 2-3 sets of 10-15 repetitions, focusing on slow, controlled movements.
- Proper Technique: Keep your spine neutral, avoid excessive hyperextension, and engage your core muscles to prevent lower back strain.
Once you can perform multiple sets comfortably with good form, you may consider progressing to additional resistance.
Intermediate Users – Increasing Resistance Gradually
Once you've built a solid foundation, you can begin incorporating light resistance to increase the challenge and further strengthen the lower back muscles.
- Use Light Weights: Start with 5-10 lbs (such as a small weight plate or a medicine ball).
- Progressive Overload: Increase resistance gradually by adding a small amount of weight each week to stimulate muscle growth without risking injury.
- Training Volume: Perform 3-4 sets of 12-15 reps, ensuring that you can complete each repetition with controlled movement and proper posture.
At this stage, focus on developing endurance and stability, ensuring that weight increases do not compromise your spinal alignment and movement control.
Advanced Athletes – Maximizing Strength and Hypertrophy
For advanced users, progressive overload and heavier resistance become key factors in improving lower back strength and muscular endurance.
- Use Heavier Weights: Hold a 15-25 lb weight plate against your chest or use a weighted vest for added resistance.
- Alternative Resistance Methods: Consider using resistance bands for constant tension throughout the movement.
- Lower Rep Range for Strength: Perform 4-5 sets of 8-12 reps with heavier resistance, ensuring that the last few reps remain challenging but manageable with proper form.
For those focused on explosive power, incorporating slower negatives (eccentric phase) and faster concentric movements can further improve muscle activation and endurance.
General Guidelines for Safe and Effective Weight Selection
Regardless of your fitness level, certain key principles apply when selecting the appropriate weight for back extensions:
Prioritize Form Over Weight: Never sacrifice form for heavier resistance—improper technique increases the risk of lower back injuries.
Adjust Based on Fatigue Levels: If you struggle to maintain proper posture by the 8th-10th rep, you may need to reduce the weight.
Listen to Your Body: Mild discomfort is normal, but sharp pain or excessive strain indicates improper weight selection or technique.
Incorporate Rest and Recovery: Strengthening the lower back requires adequate rest between sessions to avoid overuse injuries.
The best weight for the back extension machine depends on individual goals and experience level:
Beginners: Bodyweight only, focus on mastering form.
Intermediate Users: Light weights (5-10 lbs) with progressive overload.
Advanced Athletes: Heavier weights (15-25 lbs) for strength and hypertrophy.
By progressively increasing resistance while maintaining proper technique, you can maximize muscle growth, improve posture, and enhance lower back strength safely and effectively.
Types of Back Extension Machines – Pros and Cons
Back extension machines come in various designs, each catering to different fitness levels and workout preferences. Choosing the right machine depends on factors such as space availability, intensity level, range of motion, and user comfort. Understanding the advantages and drawbacks of each type can help you make an informed decision that suits your fitness goals or gym setup.
45-Degree Back Extension Machine
The 45-degree back extension machine, also known as a hyperextension bench, is one of the most commonly used back workout machines gym. Its angled design provides a moderate level of difficulty, making it suitable for both beginners and advanced users.
Pros:
- Balanced Range of Motion: The 45-degree angle offers an effective stretch and contraction for the lower back, reducing excessive strain.
- Versatile for All Fitness Levels: This machine provides adequate support, making it accessible for beginners while still challenging enough for advanced users.
- Stability and Safety: The fixed angle helps users maintain proper form, reducing the risk of hyperextension or incorrect posture.
Cons:
- Takes Up More Space: Compared to compact back extension machines, the 45-degree version requires more floor space, which may be a limitation for small gyms.
- Limited Adjustability: Some machines may lack height or angle adjustments, restricting customization for different users.
90-Degree Back Extension Machine
The 90-degree back extension machine, also known as a Roman chair, positions the user in a completely horizontal stance. This variation increases difficulty by requiring more strength and control from the lower back muscles.
Pros:
- Intensified Muscle Engagement: Due to the increased range of motion, the lower back, glutes, and hamstrings experience greater activation.
- Improves Core Stability: This machine challenges core engagement, enhancing overall strength and balance.
- Ideal for Advanced Users: Athletes and experienced lifters can benefit from the greater difficulty level of the 90-degree machine.
Cons:
- Not Beginner-Friendly: The horizontal position can be too challenging for users with weak lower back muscles or poor core stability.
- Requires More Space: Due to its longer frame, this machine can be difficult to accommodate in compact workout areas.
Horizontal Back Extension Machine
The horizontal back extension machine offers a flat, bench-like design with an adjustable support pad. This type is often found in compact gyms or rehabilitation settings, as it provides a low-impact alternative to other variations.
Pros:
- Space-Saving Design: Its compact and minimalist structure makes it perfect for small gyms.
- Safer for Beginners: Since the movement is less intense than angled machines, it’s a good starting point for those new to back extension exercises.
- Lower Risk of Injury: The horizontal position reduces the chance of excessive spinal extension, making it a safer choice for individuals with lower back concerns.
Cons:
- Limited Range of Motion: Compared to 45-degree and 90-degree machines, the horizontal version restricts movement, potentially leading to less muscle activation.
- Lower Intensity: This machine may not be challenging enough for advanced users looking to build significant lower back strength.
Selecting the right back extension machine depends on your fitness level, space availability, and workout intensity preferences.
- If you’re looking for a balanced and versatile option, the 45-degree back extension machine is a great choice.
- If you want a more intense workout with maximum range of motion, the 90-degree back extension machine is ideal.
- If you prefer a compact, beginner-friendly, and low-impact alternative, the horizontal back extension machine is the best fit.
Understanding these pros and cons will help you choose the most suitable back extension equipment to enhance your lower back strength and overall fitness.
How to Choose the Right Back Extension Machine
Selecting the right back extension machine is a crucial decision for gym owners and fitness enthusiasts. A well-chosen machine enhances lower back strength, posture, and core stability, making it an essential piece of equipment in any fitness facility. However, with multiple designs and features available, it’s important to assess key factors before making a purchase. Below is a comprehensive guide to help you choose the best back extension machine for your gym.
Assess Your Gym Space
Before investing in a back extension machine, it’s essential to consider the available space in your gym. Machines come in various sizes, and selecting one that fits comfortably within your facility ensures optimal space management and a clutter-free workout environment.
- Measure Your Gym Area: Take accurate dimensions of the space where you plan to place the machine.
- Account for User Movement: Ensure there’s enough room for users to mount, dismount, and perform exercises without feeling restricted.
- Consider Foldable or Compact Designs: If space is limited, opt for adjustable or foldable back extension machines that can be stored when not in use.
Consider User Needs and Experience Levels
Different back extension machines cater to various fitness levels, so it’s important to choose equipment that aligns with your gym members’ capabilities and training goals.
Types of Back Extension Machines:
- 45-Degree Back Extension Machine:
- Best for beginners and general gym users.
- Provides a less intense angle for lower back strengthening.
- Suitable for rehabilitation and functional training.
- 90-Degree Roman Chair (Hyperextension Bench):
- Ideal for advanced users and athletes looking for higher resistance training.
- Places more emphasis on lower back, glutes, and hamstrings.
- Requires greater core strength and balance to perform correctly.
- Adjustable Back Extension Machine:
- Offers multiple angles (adjustable from 45° to 90°) to accommodate various fitness levels.
- Provides a versatile workout experience by allowing users to gradually progress in difficulty.
If your gym caters to a diverse clientele, an adjustable back extension machine is the most versatile choice.
Check Weight Capacity and Stability
A high-quality back extension machine must be sturdy and capable of supporting various body weights to ensure safety and durability.
- Maximum User Weight: Choose a machine with a weight capacity that accommodates heavier users. A sturdy model should support at least 250-300 lbs.
- Frame Construction: Look for machines made from reinforced steel for enhanced durability. Avoid lightweight, flimsy materials that may compromise stability.
- Non-Slip Footplates and Padding: Ensure the machine has grip-enhanced foot platforms and comfortable padding to prevent slippage and discomfort during exercises.
Look for Durability and Build Quality
A durable, high-quality back extension machine is a long-term investment that minimizes maintenance costs and ensures user safety.
- Frame Material: Opt for heavy-duty steel construction for maximum strength and longevity.
- Cushioning and Upholstery: Thick, tear-resistant padding enhances comfort and prevents wear over time.
- Welded Joints and Coating: A powder-coated finish and strong welds add to the machine’s lifespan by preventing rust and structural weaknesses.
Evaluate Comfort and Adjustability
For an optimal workout experience, a comfortable and adjustable back extension machine is essential.
- Adjustable Height and Angles: Look for machines that allow users to modify the height or incline based on their body size and fitness level.
- Padded Support: High-quality foam rollers and cushioned pads reduce strain on the lower back and improve comfort.
- Ergonomic Design: Ensure that the machine aligns with the user’s natural spinal curvature, reducing unnecessary pressure on the lower back.
Compare Pricing and Value for Money
While budget is an important factor, choosing a cheap, low-quality machine may lead to frequent repairs and poor user experience.
- Compare Features vs. Cost: Higher-end machines often include adjustable angles, better durability, and higher weight capacities—features worth the extra investment.
- Avoid Low-Quality Brands: Extremely low-priced machines may compromise on stability and comfort, leading to safety risks.
- Look for Warranty Coverage: A reliable supplier should offer at least a 1-3 year warranty on the frame and parts, ensuring long-term peace of mind.
Consider Supplier Reputation and Customer Support
Choosing the right supplier ensures you receive a high-quality product with excellent after-sales support.
- Check Reviews and Ratings: Research customer feedback to verify the quality, durability, and service of the supplier.
- After-Sales Support: Opt for suppliers that offer installation assistance, maintenance guidance, and customer service.
- Warranty and Return Policy: Ensure that the supplier has a clear return policy and provides warranty coverage for defects.
Selecting the right back extension machine requires careful consideration of space, user needs, weight capacity, durability, comfort, pricing, and supplier reputation.
For Beginners and General Users: A 45-degree back extension machine provides a comfortable and accessible starting point.
For Advanced Athletes: A 90-degree hyperextension bench challenges strength and endurance.
For Maximum Versatility: An adjustable back extension machine caters to all fitness levels.
By following this guide, you can confidently invest in high-quality back extension equipment that enhances your gym’s offerings and ensures a safe, effective workout experience for your clients.
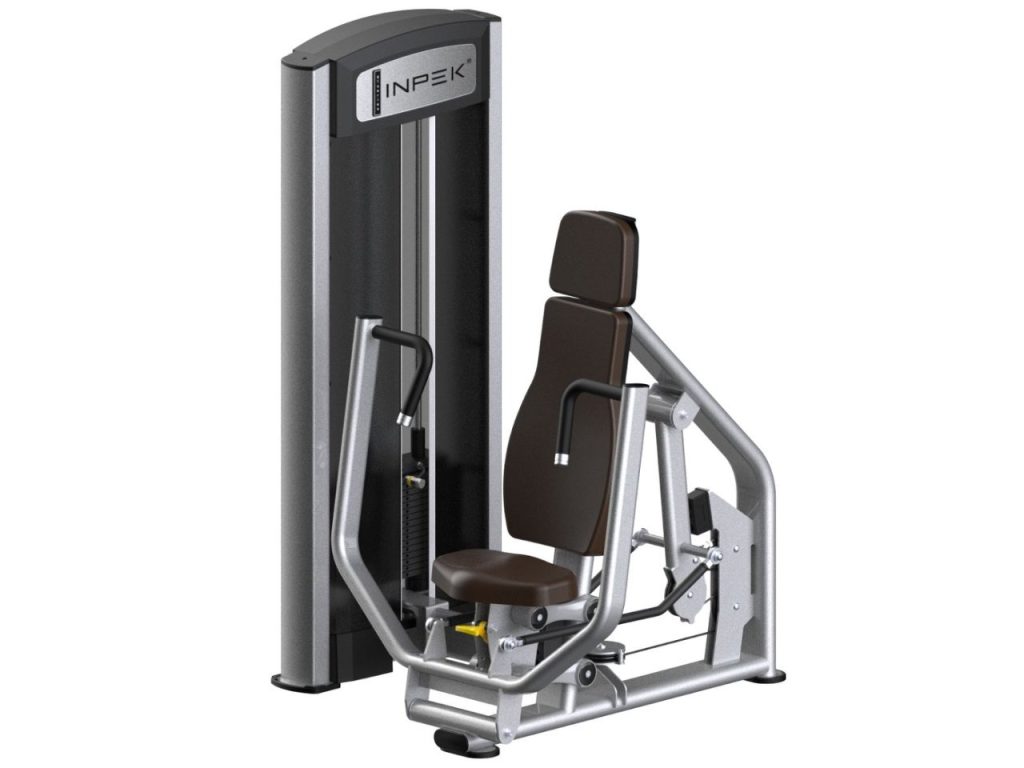


How to Use Ab Crunch Machines Correctly
Using an ab crunch machine effectively requires proper form, correct machine adjustments, and controlled movement to maximize results and avoid injury. Whether you are a beginner or an advanced gym-goer, understanding the correct posture, execution, and common mistakes will help you get the most out of this core-strengthening equipment. Below is a step-by-step guide to using an ab crunch machine correctly, along with variations and common pitfalls to watch out for.
Correct Posture and Steps
Maintaining the right posture while using the ab crunch machine is essential to ensure your abdominal muscles engage properly without straining the lower back or neck.
Positioning
- Sit on the machine with your lower back firmly pressed against the backrest for support.
- Adjust the seat height so that your knees are at a 90-degree angle and your feet are securely placed under the footpads.
- Ensure the movement arm or resistance pads are aligned with your upper chest or shoulders, depending on the machine’s design.
Grip and Alignment
- Hold onto the handles with an overhand grip, keeping your elbows slightly bent rather than locked out.
- If your machine has a chest or shoulder pad instead of handles, press against the pad with your upper torso while keeping your hands on the side grips for stability.
Executing the Movement
- Engage your abdominal muscles and slowly curl your upper body forward, bringing your chest towards your knees.
- Hold the crunch position for 1-2 seconds, ensuring you feel the contraction in your abs.
- Slowly return to the starting position in a controlled manner, avoiding sudden or jerky movements.
Breathing Technique
- Exhale as you crunch forward, contracting your abs.
- Inhale as you return to the starting position, maintaining control over the movement.
By following these steps, you can perform each repetition efficiently and safely, maximizing abdominal engagement.
Variations of the Ab Crunch Machine Exercise
The ab crunch machine offers different variations to target various sections of the core and add diversity to your workout.
Seated Ab Crunch
- This is the standard exercise performed while seated on the machine.
- It primarily targets the upper and lower abs, providing a stable and controlled movement.
Standing Ab Crunch
- Some machines allow a standing variation, requiring the user to stabilize their core while performing the crunch.
- This version engages more core muscles, including obliques and lower back stabilizers, as balance becomes a factor.
Single-Arm Crunch
- Instead of using both arms, you can perform the crunch unilaterally (one arm at a time) to focus on each side of your abs separately.
- This helps correct muscle imbalances and strengthens core stability.
These variations help keep your workout challenging and effective, ensuring continuous progress.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Incorrect technique can lead to poor results or even injuries, so it’s crucial to be aware of common mistakes and how to prevent them.
Using Momentum Instead of Muscle Engagement
- Mistake: Swinging your body or using excessive force rather than controlled muscle engagement.
- Correction: Perform slow, controlled movements, focusing on contracting your abs rather than relying on momentum.
Overloading with Heavy Weights
- Mistake: Selecting too much resistance, which can strain the lower back and lead to improper form.
- Correction: Start with lighter weights and increase gradually once you master the movement with proper form.
Incorrect Back and Neck Alignment
- Mistake: Straining your neck or arching your lower back during the movement.
- Correction: Keep your spine neutral, with your chin slightly tucked, and ensure your lower back remains supported against the pad.
Incomplete Range of Motion
- Mistake: Performing half-reps, reducing the effectiveness of the exercise.
- Correction: Move through the full range of motion, ensuring a complete crunch and controlled return to the start position.
Avoiding these mistakes will help prevent injuries and maximize the effectiveness of your ab workout.
Using an ab crunch machine correctly involves proper positioning, controlled movement, and avoiding common mistakes. By following the step-by-step guide and incorporating variations, you can effectively target your core muscles and improve overall abdominal strength. Whether you’re a beginner looking for stability or an advanced athlete aiming to intensify your routine, the ab crunch machine is an excellent tool to enhance core strength and endurance.
Ab Crunch Machines Suitable for Children
When considering fitness equipment for children, safety, proper ergonomics, and ease of use should be top priorities. While crunch machine abs can help children develop core strength and promote an active lifestyle, not all machines are designed with young users in mind. Choosing the right machine ensures that children can exercise safely and comfortably while enjoying the benefits of core training. Below, we explore the key features that make an ab crunch machine suitable for children and how they contribute to a safe and effective workout experience.
Adjustable Resistance
Resistance control is essential when selecting an ab crunch machine for children, as their strength levels vary depending on age and fitness ability.
- Easily Adjustable Weights: A suitable machine should allow for light resistance settings to prevent excessive strain on young muscles.
- Progressive Overload: The ability to gradually increase resistance helps children build core strength safely over time.
- Smooth Resistance Mechanism: A fluid motion prevents jerky or sudden movements that could lead to discomfort or injury.
Having adjustable resistance ensures that the machine grows with the child, providing a customized and manageable workout experience.
Ergonomic Design
Children have smaller frames and different proportions compared to adults, so the machine must accommodate their body size while providing adequate support.
- Adjustable Seat and Back Padding: Ensures that the child is properly positioned during the exercise, maintaining correct posture.
- Comfortable Arm and Leg Placement: Handles and footpads should be appropriately sized for smaller hands and feet.
- Supportive Backrest: Helps maintain a neutral spine position, reducing the risk of strain on the lower back.
A well-designed ergonomic machine enhances comfort, stability, and effectiveness, making workouts more enjoyable for children.
Safety Features
Since children are more prone to accidents due to inexperience, ab crunch machines designed for them should include additional safety measures.
- Built-in Safety Locks: Prevents sudden weight changes or improper usage that could cause injuries.
- Non-Slip Footpads and Handles: Ensures a secure grip and prevents the feet from slipping during the exercise.
- Controlled Range of Motion: Restricts excessive movement that could lead to hyperextension or improper form.
With these safety features in place, children can use the machine confidently and independently, reducing the risk of accidents.
Compact and Space-Saving Design
Children’s gym equipment should be practical and fit easily into a school or children’s gym area without taking up too much space.
- Lightweight and Compact: The machine should be smaller in size compared to adult versions, making it easier to fit in different environments.
- Foldable or Easily Movable: Some machines offer a folding feature or wheels for easy storage, making them convenient for multi-use spaces.
A compact ab crunch machine ensures that it can be incorporated into various fitness settings without requiring excessive space.
Ab crunch machines can be a great addition to a child-friendly fitness environment when designed with adjustability, ergonomics, safety, and space efficiency in mind. By selecting a machine that meets these criteria, parents, schools, and fitness centers can ensure a safe, effective, and enjoyable workout experience for children. Encouraging core strength development from a young age helps build healthy exercise habits, improve posture, and enhance overall physical fitness for the future.
Product Features of Inpek Fitness Ab Crunch Machines
At Inpek Fitness, our exercise machine for stomach abs are designed to provide an effective, safe, and comfortable core workout experience. Built with premium materials and innovative features, our machines cater to users of all fitness levels, from beginners to advanced athletes. Whether you are looking for a stomach exercise machine to tone your abs or a high-performance belly workout machine for strength training, our ab crunch machines are built to deliver exceptional results. Below, we break down the key features that set our equipment apart.
Adjustable Resistance for Progressive Training
A key feature of our ab crunch machines is the ability to adjust resistance levels, allowing users to customize their workouts based on their fitness level and goals.
- Multiple Resistance Settings: Our machines offer a range of weight options, making them suitable for both beginners and advanced users looking to build core strength.
- Progressive Overload: Users can increase resistance over time, ensuring continuous muscle growth and endurance improvement.
- User-Friendly Adjustments: The resistance can be modified quickly and easily, allowing for smooth transitions between different intensity levels.
This feature ensures that our ab crunch machines remain versatile and adaptable, meeting the needs of diverse gym members.
Ergonomic Design for Maximum Comfort
Comfort and safety are crucial when performing ab exercises. Our machines are designed with an ergonomic structure that supports the natural movement of the body while minimizing strain.
- Adjustable Padding and Back Support: The cushioned backrest and seat provide optimal lumbar support, reducing stress on the spine and lower back.
- Proper Body Alignment: Our design promotes correct posture, preventing users from straining their neck or shoulders during crunches.
- Customizable Fit: The adjustable seating and grips ensure that users of all heights and sizes can find their ideal positioning for maximum effectiveness.
This ergonomic approach enhances comfort and minimizes the risk of injury, making workouts more efficient and enjoyable.
Heavy-Duty Frame for Durability and Stability
Durability is a top priority when investing in gym equipment. Our ab crunch machines are constructed from high-quality, heavy-duty materials to withstand constant use in commercial gym settings.
- Premium Steel Construction: The frame is built with reinforced steel, ensuring exceptional strength and longevity.
- High Weight Capacity: Designed to accommodate users with different fitness levels, our machines can handle high-intensity workouts without wear and tear.
- Scratch-Resistant Coating: The powder-coated finish prevents rust and scratches, ensuring the machine remains in top condition for years.
This robust design ensures that our ab crunch machines provide reliable performance, even in high-traffic fitness centers.
Smooth Glide Mechanism for Seamless Movement
A smooth, controlled movement is essential for an effective ab workout. Our belly workout machines are equipped with a precision-engineered glide mechanism to provide fluid and consistent motion.
- Frictionless Operation: The machine moves seamlessly, eliminating jerky or uneven movements that could disrupt the workout.
- Enhanced Exercise Efficiency: Users can fully engage their abdominal muscles without interruptions or mechanical resistance.
- Minimal Maintenance Required: The high-quality bearings and durable construction ensure that the machine operates smoothly for years with little upkeep.
This feature allows users to focus entirely on their core workout, leading to better muscle activation and faster results.
Advanced Safety Features for Injury Prevention
Safety is a top priority at Inpek Fitness, which is why our ab crunch machines come with multiple built-in safety features to protect users from accidents or injuries.
- Safety Locks: These ensure that the machine remains secure during use, preventing accidental weight shifts.
- Non-Slip Footpads: The anti-skid design provides extra grip, preventing users from slipping while performing crunches.
- Stable Base: The machine features a wide, balanced base to prevent wobbling or tipping over, ensuring maximum stability.
These safety measures make our ab crunch machines suitable for all fitness levels, from beginners to seasoned athletes.
At Inpek Fitness, we prioritize quality, comfort, durability, and safety in all our gym equipment. Our ab trainer equipments are designed to deliver exceptional performance, whether you’re looking to tone your abs, strengthen your core, or improve your overall fitness.
Adjustable Resistance for customized workouts.
Ergonomic Design for comfort and proper posture.
Heavy-Duty Frame for long-lasting durability.
Smooth Glide Mechanism for seamless exercise motion.
Advanced Safety Features to prevent injuries.
By incorporating an Inpek Fitness ab crunch machine into your gym, you can enhance the workout experience for your clients and provide them with one of the best core training machines available.

FAQs About Back Extension Machines & Ab Crunch Machines
Are back extension machines good?
Yes, back extension machines can be effective for strengthening the lower back, specifically the erector spinae muscles. These muscles run along your spine and are crucial for maintaining posture and providing stability. When used properly, the back extension machine can help with improving flexibility and core strength. It can also assist in relieving lower back pain by enhancing muscle strength and offering postural support. However, it's important to ensure proper form while using the machine to avoid putting unnecessary stress on the spine. For best results, include it as part of a well-rounded workout routine that incorporates other core and lower body exercises.
Are back extensions bad for herniated disc?
Back extensions can be risky for those with a herniated disc if performed incorrectly. A herniated disc occurs when one of the spinal discs bulges or ruptures, potentially causing nerve compression. Back extensions, especially with poor form, can place excessive pressure on the spine, worsening the condition. However, with controlled movements and no added weight, back extensions may help strengthen the muscles surrounding the spine, offering better support and stability. It's crucial to consult with a healthcare provider before attempting back extensions if you have a herniated disc. Exercises that focus on gentle core strengthening, such as planks or bird dogs, may be better alternatives.
How often should I do back extensions?
For most individuals, performing back extensions 2-3 times a week is sufficient to strengthen the lower back muscles without overtraining. Since the muscles involved in back extensions recover relatively quickly, it's important to allow for adequate recovery between sessions. This recovery time helps prevent muscle fatigue and injury. However, the exact frequency should be adjusted based on your fitness level and goals. Beginners should start with lighter resistance and fewer sets (2-3 sets of 10-12 reps), progressively increasing volume and intensity as strength improves. Always focus on form and control rather than speed or weight to maximize safety and effectiveness.
Which exercises should I avoid with lower back pain?
If you're experiencing lower back pain, it's crucial to avoid exercises that could worsen the condition or strain the spine. These include:
- Heavy deadlifts and squats (without proper form) – These compound lifts can place a lot of stress on the lower back, especially with improper technique.
- Sit-ups or crunches – These exercises can increase pressure on the spine and worsen back pain.
- High-impact exercises like running on hard surfaces or jumping movements.
Instead, focus on core stabilization exercises like planks, bird dogs, or glute bridges to build strength without risking further injury. Always check with a healthcare provider before starting a new exercise routine with lower back pain.
Do back extensions help sciatica?
Back extensions can sometimes help with sciatica, but it depends on the underlying cause of the condition. Sciatica is often caused by pressure on the sciatic nerve, typically due to a herniated disc or spinal misalignment. For some people, strengthening the lower back and core muscles through controlled back extensions can help relieve pressure on the spine and reduce sciatica symptoms. However, if sciatica is severe or caused by specific spinal issues, back extensions could potentially exacerbate the pain. It's important to start with gentle, low-impact exercises and consult a healthcare provider for personalized recommendations to safely manage sciatica.
How much weight should I do on back extension machine?
When using the back extension machine, it's essential to start with no added weight or very light resistance until you have mastered proper form. This ensures you're not overloading your spine and risking injury. Begin with bodyweight extensions, and once you're comfortable with the movement, gradually add weight in small increments (typically 5-10 pounds). The goal is to feel the muscles in your lower back working without straining or jerking. For most people, moderate weight (10-30 pounds) will suffice for building strength once the form is mastered. Always prioritize control over heavy weights to avoid potential injury.
Are abductor machines bad?
Abductor machines are not inherently bad, but they can be less effective than other exercises for building the glutes and outer thighs. The machine isolates the abductors (muscles on the outer hips) but may not engage other important stabilizer muscles that are involved in functional movements. Additionally, improper form or excessive weight can lead to hip strain. For better overall development, it’s beneficial to incorporate a variety of exercises, such as lunges, squats, or deadlifts, which target the same muscles while also engaging other muscle groups for a more balanced workout. Using the abductor machine in moderation is fine, but it should not be the sole exercise for these muscles.
What is the best machine for back?
The best machine for strengthening the back depends on the specific muscles you wish to target. Common choices include:
- Lat pulldown machine – Great for working the lats and upper back.
- Seated row machine – Focuses on the middle back and rhomboids.
- Back extension machine – Excellent for strengthening the lower back (erector spinae).
- T-Bar row machine – Targets the upper and middle back, especially the traps and rhomboids.
Each machine offers benefits, but a combination of these exercises will provide a more balanced, comprehensive workout for the back muscles. Make sure to use proper form to avoid injury.
Do back extensions hurt lower back?
Back extensions should not hurt the lower back when performed correctly. In fact, they are designed to strengthen the muscles that support the spine, helping to reduce back pain over time. However, if performed with poor form, such as excessive arching of the lower back or using too much weight, back extensions can put excessive strain on the spine, potentially leading to discomfort or injury. Start with bodyweight back extensions and focus on controlled movement before progressing to added weight. If you experience pain during the exercise, stop immediately and consult a fitness professional or healthcare provider.
Do back extensions build muscle?
Yes, back extensions can build muscle, particularly in the lower back. By targeting the erector spinae (the muscles running along your spine), they help improve muscular endurance and strength. Regular back extension exercises can also engage the glutes and hamstrings, contributing to overall lower body strength. To see muscle-building results, focus on gradual progression, increasing the number of reps, sets, or weight over time. Ensure that you're performing back extensions with proper form to maximize muscle activation and reduce the risk of injury.
What is another name for the back extension machine?
The back extension machine is also known as the Roman chair or hyperextension bench. These terms refer to the same piece of equipment that is used to perform back extensions. The name "Roman chair" comes from the historical association with Roman gladiator training, while "hyperextension bench" refers to the action of slightly hyperextending the lower back during the exercise. Both names are widely used in gyms, but the function of the machine remains the same: to target the lower back, glutes, and hamstrings.
How to correctly do back extensions?
To perform back extensions correctly:
- Set up: Position yourself on the back extension machine with your hips resting on the padded support. Adjust the machine so your hips are slightly bent at the starting position.
- Foot placement: Place your feet securely under the footpads.
- Movement: Keeping your back straight, lower your upper body towards the ground by bending at the waist. Avoid rounding your back.
- Extension: Engage your lower back muscles (erector spinae) and raise your torso back to a neutral position, fully extending your back.
- Form: Don’t arch beyond a neutral spine or over-extend, which can put undue pressure on the spine. Perform slowly and with control.
For proper form, keep your core tight and avoid jerking motions throughout the movement. Start with bodyweight before progressing to added resistance.
Do back extensions help lower back fat?
Back extensions do not directly target fat loss in the lower back. Spot reduction (losing fat from specific areas) is a myth. To reduce lower back fat, focus on overall fat loss through a combination of:
- Strength training (including back extensions to build muscle).
- Cardio exercises (running, cycling, swimming).
- A healthy, balanced diet to create a caloric deficit.
As you lose body fat, the muscles in the lower back, strengthened by exercises like back extensions, will become more defined. However, back extensions themselves primarily improve muscular strength rather than fat loss.
How to stretch the lower back?
To stretch the lower back, try these effective stretches:
- Child’s pose: Kneel on the floor and sit back onto your heels, then reach your arms forward, letting your forehead rest on the ground. This stretches your lower back, glutes, and hips.
- Cat-cow stretch: Start on hands and knees, then alternate between arching your back (like a cat) and letting your belly drop towards the floor (like a cow), moving through the spine.
- Knee-to-chest stretch: Lie on your back and pull one knee towards your chest while keeping the other leg extended. This will stretch the lumbar spine.
- Seated forward bend: Sit with your legs straight, and reach for your toes. This stretches the lower back and hamstrings.
Are back extensions push or pull?
Back extensions are considered a "push" movement for the posterior chain. This is because you are extending your lower back, which involves a pushing motion to lift your torso upward. While traditional push exercises (like chest presses) involve pushing against resistance, back extensions involve pushing the upper body back into an extended position, engaging the erector spinae and glutes.
What muscles do reverse back extensions work?
Reverse back extensions primarily target the glutes, hamstrings, and lower back muscles (erector spinae). This exercise is performed while lying face down and lifting the legs rather than the upper body. Key muscle groups worked include:
- Glutes – Engaged as you lift your legs behind you.
- Hamstrings – Activated as you extend the hips.
- Lower back – Stabilizes during the leg lift and assists with the movement.
- Core muscles – Help stabilize your body during the lift.
Reverse back extensions are an excellent variation for strengthening the lower back while also targeting the glutes and hamstrings.
Is a 45-degree back extension better than a 90-degree back extension?
A 45-degree back extension is generally considered more effective for beginners and those focusing on lower back and core strength. It offers a safer range of motion, reducing strain on the spine. Additionally, a 45-degree angle allows for full engagement of the erector spinae, glutes, and hamstrings without over-extending the lower back.
A 90-degree back extension, where the body is positioned more upright, typically requires more strength and flexibility, as it involves a greater range of motion and can place additional stress on the spine if not performed correctly.
For most people, 45-degree extensions are optimal for building strength without excessive risk.
What is the best degree for back extension?
The ideal angle for back extensions is typically 45 degrees. This angle provides a balanced range of motion and targets the lower back (erector spinae), glutes, and hamstrings effectively. The 45-degree angle ensures you can perform the exercise with proper form and minimal strain on the spine.
For more advanced lifters, a slightly steeper angle or additional weight may be used for more challenge. However, 45 degrees is the sweet spot for most people seeking a safe and effective exercise to strengthen the lower back.
What are the benefits of 45-degree back extensions?
The 45-degree back extension offers several benefits:
- Lower back strengthening – Targets the erector spinae, which helps improve posture and reduce lower back pain.
- Glute and hamstring activation – Strengthens the posterior chain, crucial for overall strength and stability.
- Improved core stability – Engages the core to stabilize the torso during the movement.
- Safer for beginners – The 45-degree angle ensures a manageable range of motion with less strain on the spine, reducing injury risk.
This exercise is also great for people recovering from lower back injuries as it builds strength without overloading the spine.
How many times should I do back extensions?
For most individuals, performing back extensions 2-3 times a week is sufficient to see strength gains and improve lower back health. It's important to allow for recovery time between sessions since the muscles targeted in back extensions (erector spinae, glutes, hamstrings) need time to repair and strengthen.
For beginners, start with 2 sets of 10-15 reps and gradually increase volume as strength improves. Progressive overload (increasing resistance or reps) can be applied as you become more comfortable with the movement. Always prioritize form over adding weight.
What is a good substitute for 45-degree back extensions?
If you don’t have access to a 45-degree back extension machine, several effective substitutes can target similar muscle groups:
- Glute bridges – Focus on strengthening the glutes, hamstrings, and lower back.
- Roman chair back extensions – Similar movement, using a hyperextension bench, targeting the lower back muscles.
- Superman exercise – Lying face down and lifting your arms and legs off the ground to engage the lower back and glutes.
- Deadlifts – A compound movement that targets the posterior chain, including the lower back.
These alternatives help strengthen the lower back and glutes, offering variety in your workout routine.
Should you round your back on back extension?
No, you should never round your back during a back extension. Rounding places excessive stress on the spine and increases the risk of injury. Instead, focus on keeping a neutral spine throughout the movement.
When lowering your torso, ensure you’re hinging at the hips and not rounding through your back. At the top of the movement, avoid overextending; instead, bring your torso to a neutral position, fully engaging the lower back muscles. Keeping a straight back reduces the risk of strains and injury.
Is reverse hyperextension the same as back extension?
No, reverse hyperextension is different from a traditional back extension. While both exercises target the lower back, the reverse hyperextension focuses more on the glutes and hamstrings by elevating the legs instead of the upper body. It’s typically performed on a reverse hyperextension machine where the hips are supported, and the legs are lifted.
Back extensions, on the other hand, involve extending the torso from a bent position, primarily targeting the erector spinae in the lower back. Both exercises are valuable for building posterior chain strength, but they target muscles in slightly different ways.
What is normal back extension?
A normal back extension refers to the standard movement where the upper body is raised from a bent position, focusing on the lower back muscles (erector spinae), glutes, and hamstrings. It’s typically performed on a back extension machine where your hips rest on a padded support, and you extend your back to a neutral position. The goal is to increase strength in the posterior chain while maintaining good form and avoiding over-extension to prevent injury.
Should I do heavy back extensions?
Heavy back extensions can be effective for building strength in the lower back, but they should be approached with caution. Start with bodyweight back extensions or light resistance to master proper form. Adding weight too quickly can lead to poor posture, lower back strain, or injury. If you're adding weight, use a slow and controlled movement and focus on quality reps rather than heavy load. Over time, progressively increase the resistance as your muscle strength improves, but always prioritize form to avoid injury.
How to Do Back Extension Machine Correctly?
- Adjust the machine so your hips align with the pad, allowing a full range of motion.
- Position your feet flat on the platform and secure your lower body.
- Cross your arms over your chest or hold a weight plate for added resistance.
- Engage your core and slowly lower your torso forward while keeping your spine neutral.
- Stop when your body forms about a 60-degree angle, avoiding excessive rounding.
- Lift your torso back up using your lower back and glutes, stopping at a straight position (not overextending).
- Perform controlled reps, focusing on muscle engagement, not momentum.
Using proper form prevents strain on the lower back while effectively strengthening the erector spinae, glutes, and hamstrings.
Are Roman Chairs Good for Your Back?
Yes, Roman chairs (hyperextension benches) are good for strengthening the lower back, glutes, and core. They help improve posture, spinal stability, and injury prevention when used correctly. However, improper form—such as overextending the spine or using momentum—can lead to lower back strain.
For safe and effective use:
- Maintain a neutral spine throughout the movement.
- Avoid excessive hyperextension at the top.
- Start with bodyweight before adding resistance.
If you have pre-existing lower back issues, consult a professional before incorporating Roman chair exercises into your routine.
What Angle Should Back Extensions Be At?
The optimal angle for back extensions depends on machine type and experience level:
- 45-Degree Back Extension Machines (Roman Chairs) – Common in gyms, this angle provides a good balance between lower back activation and safety.
- Horizontal Back Extension Machines – These reduce spinal compression and can be easier for beginners.
- Adjustable Machines – If available, setting the angle between 45 to 60 degrees works best for muscle engagement while avoiding excessive spinal stress.
Regardless of the angle, maintain a neutral spine and controlled movement to prevent injury.
Do Back Extension Machines Work Glutes?
Yes, back extension machines engage the glutes, especially when using the right technique. To target the glutes more effectively:
- Engage your glutes at the top of the movement.
- Keep your feet turned slightly outward.
- Perform controlled reps rather than relying on momentum.
- Try a glute-focused variation by keeping your spine neutral and driving the motion with your hips instead of your lower back.
For even greater glute activation, consider adding resistance bands or holding a weight plate.
What Are the Cons of Back Extension Machines?
While effective, back extension machines have some drawbacks:
- Risk of Overextension – Excessively arching the lower back can lead to lumbar strain.
- Not Suitable for All – People with lower back injuries may find back extensions uncomfortable or unsafe.
- Can Lead to Muscle Imbalances – Overusing back extensions without strengthening the core can cause muscle imbalances.
- Limited Range of Motion – Machines restrict movement, potentially limiting effectiveness compared to free-weight exercises.
To minimize these risks, use proper form, avoid excessive weight, and balance your routine with core and glute exercises.
How Can I Improve My Back Extensions?
To improve back extensions:
- Strengthen Core Muscles – A strong core supports the lower back and prevents strain.
- Use Progressive Overload – Gradually increase resistance or reps to build strength.
- Engage Glutes & Hamstrings – Avoid relying solely on the lower back by activating surrounding muscles.
- Perform Controlled Reps – Slow, controlled movements improve muscle engagement.
- Incorporate Variations – Try weighted extensions, single-leg extensions, or stability ball extensions for variety.
Improving flexibility and mobility in the hips and hamstrings also enhances performance.
When Should You Avoid Back Extensions?
Avoid back extensions if you have:
- Lower back injuries (such as herniated discs or severe sciatica).
- Poor form or pain during the exercise.
- Existing spinal conditions that could worsen with hyperextension.
- Weak core muscles, which may increase lumbar strain.
If you experience discomfort, consult a professional before continuing back extensions. Modifications, such as partial range movements or core-focused alternatives, can help reduce strain.
Do Back Extensions Decompress the Spine?
Yes, back extensions can help decompress the spine by strengthening the erector spinae and core, which supports spinal alignment. However, excessive hyperextension or incorrect form may increase spinal compression instead.
For better spinal decompression:
- Focus on controlled movements.
- Pair back extensions with mobility exercises (such as cat-cow stretches).
- Use hanging decompression exercises (like dead hangs or inversion therapy).
Properly performed back extensions contribute to spinal health and posture improvement.
How Many Times a Week Should You Do Back Extensions?
For optimal results, 2-4 sessions per week are ideal, depending on your fitness level:
- Beginners – 2 sessions per week.
- Intermediate/Advanced – 3-4 sessions per week, depending on recovery.
Avoid overtraining by allowing at least 48 hours of rest between sessions, especially if using heavy resistance. Pairing back extensions with core and glute exercises ensures balanced strength.
Are Backbends Bad for Your Back?
Backbends can be beneficial or harmful, depending on execution and flexibility:
Benefits:
- Improve spinal mobility and flexibility.
- Strengthen the lower back and core.
Risks:
- Excessive arching can stress the lumbar spine.
- Lack of warm-up increases injury risk.
- Poor form may cause disc compression.
If performing backbends, focus on gradual progression, proper warm-ups, and core stability to avoid strain. If you have pre-existing back conditions, consult a specialist before attempting deep backbends.
How to Get a Six Pack?
Getting a six-pack requires a combination of low body fat percentage, core exercises, and a proper diet. The key steps include:
- Reduce Body Fat – Abs become visible at 10-12% body fat for men and 18-20% for women.
- Strengthen Core Muscles – Exercises like ab crunch machines, hanging leg raises, and planks help build definition.
- Eat a Clean Diet – Focus on high-protein, nutrient-dense foods while avoiding excessive processed sugars.
- Incorporate Cardio – High-intensity interval training (HIIT) and steady-state cardio help burn calories.
- Stay Consistent – A six-pack requires dedicated effort over time.
Simply using an ab crunch machine alone won’t get a six-pack. A combination of diet, resistance training, and fat loss strategies is essential.
Does the AB Crunch Machine Burn Belly Fat?
No, the ab crunch machine does not burn belly fat directly. Fat loss happens through an overall calorie deficit, not from targeted exercises (spot reduction is a myth). While the machine helps strengthen and define the abs, it won’t reduce belly fat without:
- A caloric deficit (burning more calories than consumed).
- A mix of cardio, resistance training, and a balanced diet.
- Lowering total body fat percentage through consistent exercise and nutrition.
The ab crunch machine is useful for ab muscle development, but fat loss requires full-body efforts.
Can I Do 100 Crunches a Day to Lose Belly Fat?
No, doing 100 crunches a day alone will not reduce belly fat. Spot reduction doesn’t work—fat loss happens throughout the body, not just in the area you’re working. While ab crunches strengthen your core, they don’t burn significant calories or shed fat effectively.
To lose belly fat, focus on:
- Caloric deficit (diet control).
- Full-body workouts (strength training and cardio).
- HIIT or steady-state cardio for higher calorie burn.
Crunches can enhance muscle definition, but a proper fat-loss strategy is needed for a flatter stomach.
What Burns the Most Belly Fat?
The best exercises for burning belly fat involve full-body movements that increase heart rate and calorie burn:
- HIIT workouts – Short bursts of intense exercise, such as sprints or burpees.
- Strength training – Compound exercises like deadlifts, squats, and kettlebell swings burn calories and boost metabolism.
- Cardio exercises – Running, cycling, rowing, or using stair climbers.
- Core engagement workouts – Planks, hanging leg raises, and weighted ab exercises.
The key is caloric deficit—no exercise alone can target belly fat without dietary changes.
Will Crunches Flatten My Stomach?
Crunches strengthen and tone the abdominal muscles, but they won’t flatten your stomach alone. A flat stomach comes from:
- Losing overall body fat through a caloric deficit.
- Eating a healthy diet to avoid excess fat storage.
- Incorporating full-body workouts to burn calories.
Crunches should be part of a balanced fitness routine, but they won’t replace the need for cardio and a proper diet.
How to Lose Belly Fat in 2 Weeks?
Losing a significant amount of belly fat in just two weeks is challenging, but you can make progress with:
- Cutting out processed foods – Reduce sugar, refined carbs, and high-calorie junk food.
- Increasing protein and fiber intake – Helps with satiety and muscle preservation.
- Doing HIIT workouts – Burns fat efficiently in short periods.
- Strength training – Boosts metabolism and fat loss.
- Drinking more water – Reduces bloating and aids digestion.
While noticeable fat loss takes longer, these strategies can kickstart progress.
Do Crunches Slim Your Waist?
Crunches can tone your abs, but they won’t make your waist smaller unless you reduce body fat. If you only do crunches without diet control or full-body exercise:
- Your abs may become stronger, but they won’t be visible.
- Your waist may not appear slimmer without fat reduction.
For a slimmer waist, combine strength training, cardio, and proper nutrition.
What Exercise Machine Burns the Most Belly Fat at the Gym?
The best machines for burning belly fat include:
- Treadmill (HIIT or incline walking) – Burns high amounts of calories.
- Rowing Machine – Engages full-body muscles.
- Stair Climber – Strengthens legs while increasing heart rate.
- Elliptical Trainer – Low impact, effective fat-burning cardio.
While ab crunch machines help tone abs, they don’t burn as many calories as cardio-based machines.
Is Ab Crunch Machine Worth It?
Yes, the ab crunch machine is worth it if you:
- Want to target and strengthen your abs effectively.
- Prefer a controlled movement to avoid strain.
- Want to add resistance for progressive overload.
However, it shouldn’t be your only core exercise. Mix it with planks, leg raises, and functional core training for best results.
Is Crunch Better Than Sit-Ups?
Crunches are safer and more effective than sit-ups for targeting the abs because:
Crunches focus on the rectus abdominis with minimal lower back strain.
Sit-ups engage hip flexors more than abs, increasing lower back stress.
Crunches are better for isolating the abs, while sit-ups are more of a full-core movement. If you have lower back issues, crunches are the better option.
Are Crunches Better Than Planks?
Both exercises have benefits, but they serve different purposes:
- Crunches isolate the rectus abdominis, strengthening the front of the core.
- Planks engage the entire core, including obliques and deep stabilizers.
For a stronger core and better overall function, planks are more effective. However, crunches are useful for direct ab muscle activation. A combination of both is best for a well-rounded core workout.
Are ab crunch machines effective?
Yes, ab crunch machines can be effective in targeting the abdominal muscles, specifically the rectus abdominis (the muscles you see as a "six-pack"). The machine works by allowing you to perform controlled crunches, which are a direct ab exercise. Using a machine can help ensure proper form and prevent strain on the lower back, especially for beginners or those with difficulty engaging the core in free-weight exercises. However, like all exercises, it should be combined with a well-rounded fitness routine, including cardio and a healthy diet, to reduce body fat and reveal your abs. Additionally, a variety of exercises targeting the core is ideal for optimal muscle development.
Is it OK to do ab crunches every day?
While it’s technically okay to do ab crunches every day, it’s important to allow time for muscle recovery. The abdominals are a muscle group like any other, and they need recovery time to grow and get stronger. Doing ab crunches every day without adequate rest can lead to overtraining, resulting in diminished returns and increased risk of injury. Typically, 2-4 times a week is enough to see results, with at least 48 hours of rest in between sessions. Focus on quality, controlled movements rather than frequency for better results. Additionally, combine ab exercises with full-body workouts for balanced muscle development.
Can you get abs from ab crunch machine?
The ab crunch machine can help develop the rectus abdominis (the muscles that make up your "six-pack"), but visible abs also depend on reducing body fat. The machine effectively targets and strengthens the abs, but if you want visible results, you’ll need to incorporate overall fat loss strategies, such as cardio, a caloric deficit through diet, and full-body strength training. Spot reduction (losing fat in one area) is not possible, so focus on reducing overall body fat to reveal toned abdominal muscles. Use the ab crunch machine as part of a balanced workout routine for best results.
How many sets should I do on abdominal crunch machine?
For most people, 2-4 sets of 12-15 reps on the abdominal crunch machine is effective for building strength and endurance in the abdominal muscles. If your goal is to tone your abs, aim for higher reps (15-20) with moderate resistance. For strength-building, lower reps (8-12) with more weight may be beneficial. Always focus on performing the exercise with proper form, ensuring that your core is fully engaged and avoiding jerky or rapid movements. Rest for 30-60 seconds between sets to give your muscles time to recover.
What machine is best for abs?
While several machines can target the abdominals, the ab crunch machine is one of the best for isolating the rectus abdominis. Another effective machine for abs is the cable machine (for exercises like cable crunches), which allows for a variety of ab exercises and engages the core in a dynamic way. The captain's chair machine also works great for targeting the lower abs, as it allows for leg lifts. Combine different machines and movements for a comprehensive abdominal workout, ensuring all parts of the core are engaged.
What is the most effective crunch for abs?
The most effective crunch for abs depends on your goals and form. The ab crunch machine is highly effective for targeting the upper abs as it isolates the muscle group and helps maintain form. For a more comprehensive ab workout, try combining the crunch with other movements, such as:
- Bicycle crunches (for obliques and upper abs)
- Reverse crunches (for the lower abs)
- Cable crunches (for overall ab development and resistance variation)
These exercises can work all areas of the rectus abdominis and obliques, making them effective for sculpting and strengthening the entire core.
How much weight should I use on the ab crunch machine?
The weight you use on the ab crunch machine will vary depending on your fitness level. Beginners should start with a light weight or just use the machine without any additional resistance to focus on mastering form. As you become more experienced, you can gradually increase the weight to challenge your muscles. Aim for a weight that allows you to complete 12-15 reps with proper form, where the last few reps feel challenging but not impossible. Avoid using too much weight, as it can compromise form and lead to injury. As you progress, continue to adjust the weight to match your strength and goals.
How to target bottom abs?
To specifically target the lower abs, try exercises that involve leg movement, as this engages the lower part of the rectus abdominis. Some effective exercises include:
- Reverse crunches – Lying on your back, curl your hips up toward your chest, engaging the lower abs.
- Leg raises – Raise your legs while keeping them straight to activate the lower abdominal muscles.
- Captain's chair leg lifts – Using the captain’s chair machine, lift your legs while keeping your back supported to target the lower abs.
Incorporating these exercises into your routine, along with an overall body fat-reduction plan, will help strengthen and define your lower abs.
Top 10 high-tech manufacturing hubs
End-to-end integrated manufacturing, fully integrated recycling production line
You see more than just a factory
Intelligent steel pipe production line
Next generation laser cutting technology
Intelligent pipe bending process
Intelligent mechanical welding
New generation spraying process system
Delivering superior quality through pre-assembled solutions
Our Valued Clients







Collaborate with Inpek Fitness Experts for Your Commercial Gym Projects
Looking to enhance your gym with premium equipment? Have inquiries or ideas? Complete the form below to engage with our expert team. We’ll work with you to realize your fitness facility goals efficiently and effectively.


































